Using Excel VBA write to Text file
The following examples show how to read and write from/to text files using Excel VBA and the Microsoft Scripting runtime library.
Writing to text file with Excel VBA
' Note: enable 'Microsoft Scripting runtime' Object library to your project before running this suroutine
Dim fso As Scripting.FileSystemObject
Dim ts As Scripting.TextStream
Set fso = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
' Create a text file, and return a reference to a TextStream
Set ts = fso.OpenTextFile("c:\trash\junk.txt", ForWriting)
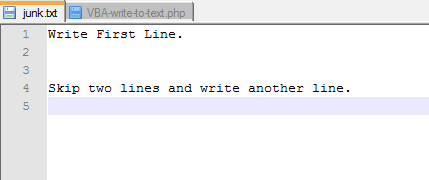
ts.WriteLine "Write First Line."
ts.WriteBlankLines 2
ts.WriteLine "Skip two lines and write another line."
ts.Close
Set ts = Nothing
Set fso = Nothing
Some VBA vocabulary
FileSystemObject The File System Object (FSO) model provides an object-based tool for working with folders and files. It allows you to use the familiar object.method syntax with a rich set of properties, methods, and events to process folders and files. The FSO model gives your application the ability to create, alter, move, and delete folders, or to determine if and where particular folders exist. It also enables you to get information about folders, such as their names and the date they were created or last modified.
TextStream The TextStream Object facilitates sequential access to a text file. The FileSystemObject(FSO) returns TextStream object when you open or create a text file. You need to reference 'Microsoft Scripting runtime' Object library to your project before using TextStream object.
OpenTextFile Opens a specified file and returns a TextStream object that can be used to read from or append to the file. Parameters:
| object: | Required. Always the name of a FileSystemObject. |
| filename: | Required. String expression that identifies the file to open. |
| iomode: | Optional. Can be one of three constants: ForReading, ForWriting, or ForAppending. |
| create: | Optional. Boolean value that indicates whether a new file can be created if the specified filename doesn't exist. The value is True if a new file is created, False if it isn't created. If omitted, a new file isn't created. |
| format: | Optional. One of three Tristate values used to indicate the format of the opened file (TristateTrue = -1 to open the file as Unicode, TristateFalse = 0 to open the file as ASCII, TristateUseDefault = -2 to open the file as the system default). If omitted, the file is opened as ASCII. |
WriteLine Writes data to a sequential file. WriteLine inserts a newline character (that is, a carriage return/line feed, or Chr(13) + Chr(10)), after it has written the final character in Output to the file.
WriteBlankLines Writes a specified number of newline characters to a TextStream file.
output:
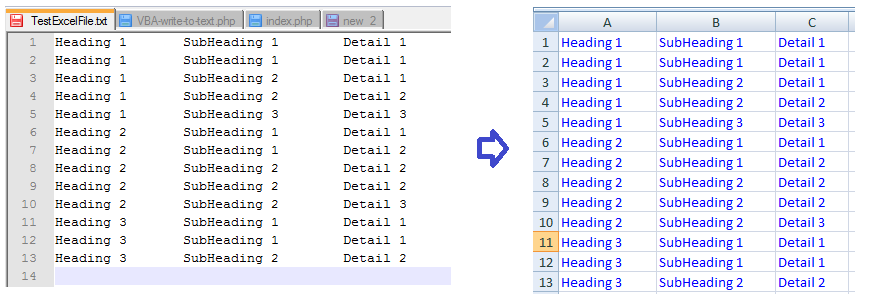
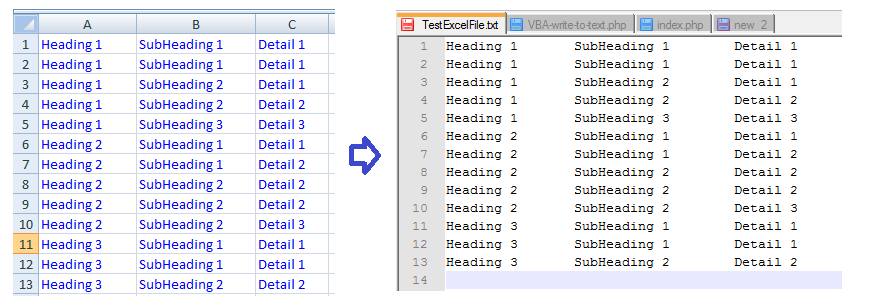
Read from an open Excel file into text file
This code reads from open excel spreadsheet and writes to a text file.
Dim fso As Scripting.FileSystemObject
Dim ts As Scripting.TextStream
Dim r As Range
Dim ColumnCount As Integer
Dim i As Integer
Set fso = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
' Open for writing
Set ts = fso.OpenTextFile( _
Environ("UserProfile") & "\Desktop\TestExcelFile.txt", ForWriting, True)
' activate Sheet1
Sheet1.Activate
' determine number of columns to copy
ColumnCount = Range("A1", Range("A1").End(xlToRight)).Cells.Count
' iterate through rows and columns
For Each r In Range("A1", Range("A1").End(xlDown))
For i = 1 To ColumnCount
ts.Write r.Offset(0, i - 1).Value & vbTab
If i < ColumnCount Then ts.Write vbTab
Next i
ts.WriteLine
Next r
ts.Close
Set fso = Nothing
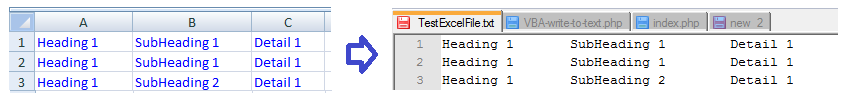
input and output:
Read from text file into Excel file
This code reads from a text file into an open Excel spreadsheet.
Dim fso As Scripting.FileSystemObject
Dim ts As Scripting.TextStream
Dim TextLine As String
Dim TabPosition As Integer
Set fso = New Scripting.FileSystemObject
' Create a text file, and return a reference to a TextStream
Set ts = fso.OpenTextFile(Environ("UserProfile") & "DesktopTestExcelFile.txt")
Workbooks.Add
Do Until ts.AtEndOfStream
TextLine = ts.ReadLine
TabPosition = InStr(TextLine, vbTab)
Do Until TabPosition = 0
ActiveCell.Value = Left(TextLine, TabPosition - 1)
ActiveCell.Offset(0, 1).Select
TextLine = Right(TextLine, Len(TextLine) - TabPosition)
TabPosition = InStr(TextLine, vbTab)
Loop
ActiveCell.Value = TextLine
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).End(xlToLeft).Select
Loop
Set ts = Nothing
Set fso = Nothing
input and output: